With inclusive education, all children are involved in the process of obtaining knowledge, regardless of their mental, intellectual and physical characteristics. Such children have the opportunity to attend general education schools at their place of residence together with their healthy peers. However, considering their special needs in education, they receive special support. All participants in the process adhere to an equal attitude towards all children, therefore any discrimination is excluded, but with the obligatory provision of special conditions for children with disabilities.
The purpose of the GEF for children with disabilities
The introduction of children with disabilities into the community is the main task of the correctional assistance system. The program and methodological manual accompanying the introduction of inclusive education in educational organizations is designed to address issues related to the education and upbringing of children who have other, special needs along with ordinary ones. In the Federal State Educational Standard of General Education, a note was made in the program of correctional work: it is developed if there are children with disabilities in the educational organization.
Thus, the GEF HIA with corrections, the latest version of 2016, is aimed primarily at correcting negative aspects in the psychological or physical development of children and indicates ways to solve problems in mastering the main curriculum. It contains recommendations for helping and supporting children in this category.

Purpose of the program:
- To identify and meet all the needs of students with disabilities in their assimilation of the BLO.
- Integrate them into educational process.
- To implement a comprehensive and individually oriented psychological and pedagogical support for training, taking into account the state of health of children with disabilities.
- Create special conditions for education and development.
- Create favorable conditions for communication and learning activities.
Difficulties in the implementation of inclusive education, described in the standard of the Federal State Educational Standard for HIA
In our society, the vast majority still perceives people with disabilities as something non-standard, foreign, and children with disabilities are often recognized as unteachable. School leaders and teachers are not sufficiently aware of the problems of such children and are not prepared to include them in the process of mastering knowledge in regular classes. Parents do not know and do not defend the rights of their disabled children, indicated in the Federal State Educational Standard for children with disabilities 2016, which can be downloaded and studied on special sites.
After all, inclusive education is not only the physical presence of children with disabilities in classes with other children, but also a change in the school itself, a change in the relationship between teachers and students participating in the educational process. There should be close cooperation between parents and teachers, involvement of parents in the learning process.
GEF standard for children with disabilities
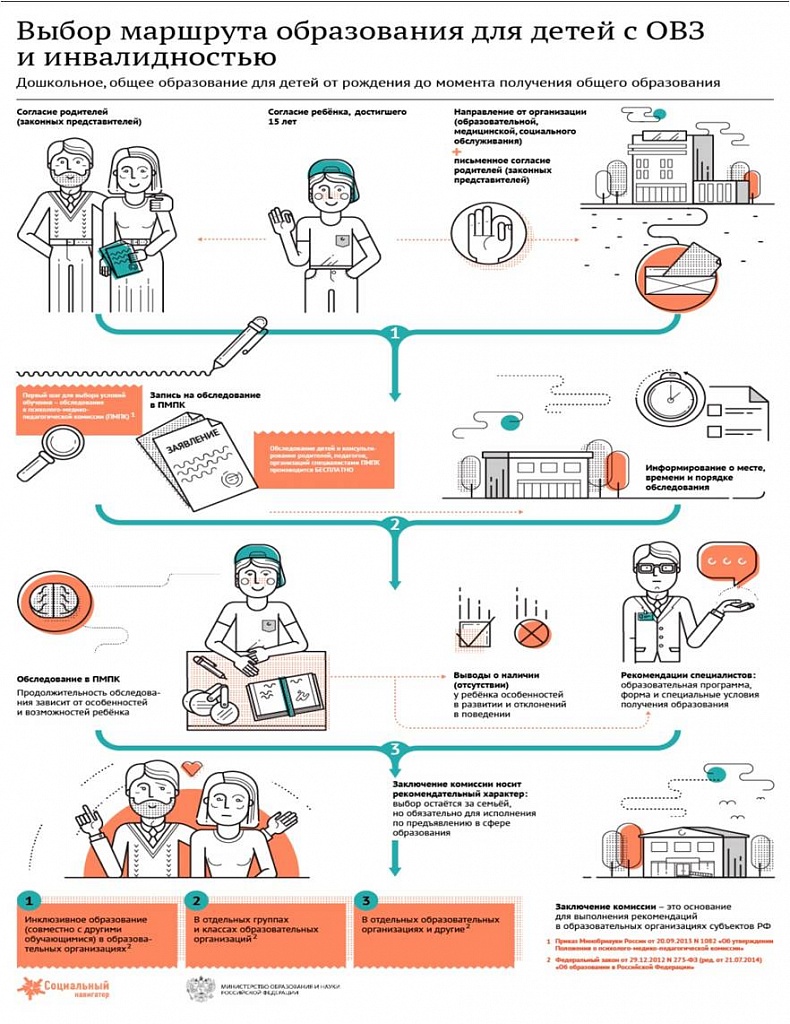
The Federal Law (clause 6, art. 11) provides for the right to compulsory education for children with disabilities and the requirements for the learning process are included in special educational standards.
The following options for educational programs are offered:
- The program is intended for children with diagnosed hearing and vision impairments and without intellectual disabilities, who are fully included in the educational stream. The main educational program for students with disabilities is mastered as part of correctional work (inclusion). An individual curriculum is available.
- The program is designed for children with mental retardation, visual, hearing, or speech disorders of varying severity. Children with disabilities receive education together with healthy peers. The process is carried out in other calendar terms, determined by the GEF standard for children with disabilities in 2016. Training can also take place in separate classes or organizations.
- The program is designed for children diagnosed with mental retardation. The education these children receive is not comparable to that of their peers. It is recommended to create several curricula and individualize the provisions of the program.
- The program is designed for children with disabilities who have complex or multiple developmental disabilities. Education takes place according to an adapted program, which is based on an individual curriculum.
In the process of training according to the FSES HVZ standard, special educational programs s, special learning programs, special educational and didactic aids. Permissible stress levels, which are determined with the help of medical professionals, must be observed.
Please note that in accordance with the Federal Law N 273-FZ "On Education in the Russian Federation", organizations engaged in educational activities organize the training and education of students with disabilities both together with other students and in separate classes or groups.
Pedagogical activity in accordance with the new Federal State Educational Standard requires the teacher to have a system of special knowledge in the field of anatomy, physiology, special psychology, defectology and social work.
Only now you can take distance learning directly on the website "Infourok" with 40% discount on the course of advanced training (72 hours). Upon completion of the course, you will receive a printed certificate of advanced training in the established form (delivery of the certificate is free).
Presentation on the topic "Implementation of the GEF for students with disabilities"
Library
materials

























26 1
Description of the presentation on individual slides:
slide number 1

Description of the slide:
issues of implementation of the fgos of students with handicapped of health in the conditions of a general educational organization MBOU secondary school No. 43 Speaker of the deputy director for water resources management Parastaeva I.Yu.
slide number 2

Description of the slide:
Relevance. One of the most important tasks of basic general education in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard is to provide conditions for the individual development of all students, especially those who are most in need of special learning conditions - children with disabilities.
slide number 3

Description of the slide:
slide number 4
![]()
Description of the slide:
Everyone has their own way! Inclusion in a general education organization Separate organizations that carry out educational activities on adapted basic general education programs Implementation of educational programs using e-learning and distance learning technologies, family education
slide number 5

Description of the slide:
Normative and legal support for obtaining a quality education for children with disabilities Constitution of the Russian Federation, Art. 43 Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, Art. 24 GEF IEO students with disabilities. Federal Law of December 29, 2012 No. 273-FZ “On Education in the Russian Federation”, Articles 11, 79 Regulatory and methodological documents of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation and other regulatory legal acts. An exemplary AOOP developed on the basis of the Federal State Educational Standard for children with disabilities
slide number 6

Description of the slide:
GEF IEO students students with HIA Standard is a set of mandatory requirements for the implementation of adapted basic general education programs of primary general education (hereinafter - AOOP IEO) in organizations engaged in educational activities (hereinafter - organization). The standard applies to legal relations that arose from September 1, 2016; training of persons enrolled before September 1, 2016 for training in adapted educational programs is carried out according to them until the end of training.
slide number 7

Description of the slide:
The standard ensures the formation of the student's personality, taking into account his special educational needs by developing his individual abilities, positive motivation and skills in educational activities. Purpose of the Standard (FSES with HIA)
slide number 8

Description of the slide:
Specifics of the requirements of the standard requirements for the final achievements of students by the time they complete school education requirements for the structure of an adapted educational program the structure of an individual special educational program requirements for the conditions for obtaining education
slide number 9

Description of the slide:
The Federal State Educational Standard for students with disabilities is the basis of the AOOP IEO The adapted educational program for students with disabilities is an educational program that takes into account the peculiarities of psychophysical development, individual capabilities, and special educational needs of students with disabilities. The development of the AOOP is based on the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard and curricula for the subjects of the curriculum. AOOP provides comprehensive correction/compensation for developmental disorders and social adaptation.
slide number 10

Description of the slide:
Requirements for the structure of the AOEP IEO The AOEP IEO for students with disabilities is developed independently in accordance with the Standard and taking into account the exemplary AOOP IEO, taking into account the special educational needs of groups or individual students with disabilities on the basis of specially developed curricula, including individual ones, that ensure the development educational program. 2.6. AOOP IEO includes a mandatory part and a part. The ratio of parts is determined depending on the AOOP LEO variant and is: 80% and 20%, 70% and 30% or 60% and 40%. 2.7. AOOP IEO is implemented by the organization through the organization of classroom and extracurricular activities. 2.8. AOOP IEO should contain three sections: target, content and organizational.
slide number 11

Description of the slide:
An explanatory note that discloses: the goals and objectives of the AOEP, the period for mastering the AOOP, the psychological and pedagogical characteristics of students (requirements for the development of students). Planned results of mastering AOOP by students. Syllabus. The program for the formation of universal educational activities for students with disabilities at the stage of primary general education. Programs of individual subjects, courses. Spiritual and moral development program Program for the formation of ecological culture, a healthy and safe lifestyle; Correctional program. The system for assessing the achievement by students of the planned results of mastering the adapted basic educational program; Program of extracurricular activities. Conditions for the implementation of the BEP: personnel conditions, financial and economic conditions, material and technical conditions, educational and methodological conditions. Requirements for sections of AOOP
slide number 12

Description of the slide:
on the basis of the Federal State Educational Standard of Primary General Education for Children with Disabilities of the Russian State Pedagogical University. A.I. Herzen developed AOOP projects for all categories of children and the timing of the assimilation. GEF NEO FOR DEAF STUDENTS (Project) (Draft) GEF IEO FOR CHILDREN WITH MENTALLY RELATED DEVELOPMENT (Draft)
slide number 13

Description of the slide:
Variants of the programs provided by the Federal State Educational Standard Option of the standard Program One (A) The main educational Program, the structure of which must include the Corrective Work Program. Second (B) Adapted educational program, which, if necessary, is individualized. (remedial school or class) Third (C) An adapted educational program that is individualized as needed. Fourth (D) Adapted core curriculum based on an individual curriculum.
slide number 14

Description of the slide:
Variants of educational programs based on the Federal State Educational Standard for children with disabilities The variant of the educational program (A) is intended for students with disabilities who have reached a level of development close to the age norm by the time they enter school; A student with disabilities in this option masters the BEP, has the right to pass the current, intermediate and state final certification. following the results of mastering the program receives a certificate of secondary education.
slide number 15

Description of the slide:
Variant of the educational program (C) A student with disabilities receives an education comparable in terms of final achievements by the time of completion of school education with the education of healthy peers, but in a longer calendar period, which is determined by the Standard. A student with disabilities mastering option B has the right to pass the current, intermediate and state final certification in other forms.
slide number 16

Description of the slide:
The third version of the educational program (C) A student with disabilities receives an education that is not comparable in terms of final achievements by the time of completion of school education with the education of peers without health restrictions, in a more prolonged calendar period, which is determined by the Standard for each category of students. Organization is required special conditions training and education for the implementation of both general and special educational needs. Based on the Standard, an adapted educational Program is created, which, if necessary, is individualized. Several curricula are created for the educational Program, including individual curricula.
slide number 17

Description of the slide:
The fourth version of the educational program (D) A student with disabilities (with complex and multiple developmental disorders) receives education according to an adapted basic educational program created on the basis of an individual curriculum. With a significant content of the "academic" component of education, maximum deepening into the field of development of life competence is required. Mandatory is the special organization of the student's environment for the realization of his special educational needs, the development of his life competence in different social environments (educational, at home, etc.)
slide number 18

Description of the slide:
In the process of schooling, the child retains the possibility of moving from one version of the standard to another (the basis for this is the conclusion of the PMPK)
slide number 19

Description of the slide:
Who determines the version of the educational program for SFGOS? The determination of the AOOP IEO option for a student with disabilities is carried out on the basis of the recommendations of the PMPK, formulated on the basis of the results of his complex psychological, medical and pedagogical examination, if the student has a disability, taking into account the IPR and the opinion of parents (legal representatives).
September is coming to an end, the educational process is in full swing in schools, but for most teachers this year it is not quite usual, because new Federal State Educational Standards (FSES) for students with disabilities (HVZ) and separately FSES for children are starting to operate With mental retardation(UO). According to the law on inclusive education, sick children will study in the same high school with healthy children. To do this, it is necessary to comply with certain conditions for the implementation of standards in the school education system, which we will discuss in detail.
Goals and objectives of the modern school
It's no secret that sick children are now born many times more than healthy ones. For society, the task becomes urgent: how and where to train them. In connection with the recognition of the value of any person, regardless of his achievements and abilities, the school is moving to inclusive education, where a disabled child is involved in society on an equal basis with healthy child. But school inclusion also needs significant changes, so there is an urgent need to standardize and systematize the education, development and upbringing of the younger generation. It is not possible to teach according to the template today, due to annually changing circumstances. The system-activity approach in education implies the teacher's ability to change "on the go", to be mobile, situationally oriented and competent in many areas of knowledge. And also adapt to children with special needs. educational needs. The task is not easy, but time forces us to change the approach to students, increasingly relying on the individual.
Options for educational programs for children with disabilities
The Federal State Educational Standard for children with disabilities and UO was introduced only in elementary school and approved by order of the Ministry of Education and Science of Russia dated December 19, 2014 No. 1598 and No. 1599 (for children with mental retardation). All students with disabilities were divided into categories:
visually impaired;
hard of hearing and late deaf;
with disorders of the musculoskeletal system (NODA);
delayed mental development(ZPR);
with severe speech disorders (SNR);
with autism spectrum disorders (ASD).

For each student with disabilities, the school is obliged to develop an individual adapted basic general education program (ABEP). Up to 4 program options can be applied to each category of schoolchildren with health problems.
For the deaf, blind, children with autism spectrum disorders and with disorders of the musculoskeletal system, there are 4 options for program requirements.
1 option. A disabled child receives an education that fully corresponds in the final section to the results that his healthy classmate shows in the same time frame, by the time of completion elementary school(grades 1-4).
Option 2. A student with disabilities receives an education that partially corresponds to the planned results shown by his peer at the end of primary school. This option involves extending this child's education by one year (grades 1-5).
3 option. A deaf, blind or mildly mentally retarded student receives an education that is not commensurate in content and final achievements with the planned results obtained by children who do not have health limitations. The terms of study can be extended by one year (grades 1-5).
4 option. A student (with a severe degree of mental retardation, blind, deaf or with complex developmental disorders) receives an education that does not correlate in terms of achievements and content with the planned results shown by his classmates without disabilities. This option allows for an extension of the terms of study from grades 1 to 6 (6 years).
For the category of hearing impaired, late deaf and visually impaired children will have three options for adapted programs for children of the above categories: ASD, GCD, deaf and blind.

And for students diagnosed with “severe speech impairment (SSD)” and “mental retardation (MPD)”, the following two options for AOOP will apply.
1 option. For children with mental retardation: they receive an education that fully corresponds to the results by the time the initial education is completed with the planned results achieved by their classmates who do not have health restrictions in the same time frame (grades 1-4). For children with SLD: they receive an education that fully corresponds to the achievement of the planned results by the end of primary school, shown by children who do not have speech impairments, in terms from 1 to 4 classes.
Option 2. Children with mental retardation will receive education at the same time as their peers without developmental disabilities (grades 1-4), subject to additional psychological and pedagogical support and special attention to the formation and development of the necessary skills. Children with SLD also receive an education that matches that of their peers, provided that an additional class is introduced, where increased attention will be paid to the development of speech. Speech children can study both in a separate class and among peers with normal speech development. Training periods can be extended as needed. The Psychological-Medical-Pedagogical Commission (PMPC) will evaluate and regulate the development of children with mental retardation and mental retardation. It is possible to transfer children of one category within the variants of adapted programs.
For children with mental retardation separate versions of the AOOP provided by the Federal State Educational Standards for children with intellectual disabilities have been developed. It takes into account the severity and depth of mental retardation, as well as a combination of various developmental disorders, and as a result, the level of readiness of the student to be included in the educational process. There are two options for AOOP for children with MR.
1 option. A child with a mild degree of mental retardation receives an education that does not correspond to the planned results applicable to a normally developing peer. Consequently, the terms of training are extended depending on the indicators for several years.
Option 2. A student with moderate, severe and profound mental retardation, as well as those with other developmental disabilities, receives basic knowledge that does not correspond, according to the final assessment, to the planned results achieved by his peer who does not have developmental disabilities at the end of schooling. The study period is extended. hallmark this option is the multiplicity of developmental disorders of the child, the combination of SV with NODA, hearing impairment, visual impairment, autism spectrum disorders. Most children are homeschooled.
The requirements for documenting, the structure and conditions for the implementation of the adapted program have changed, so school teachers will have to work hard to somehow systematize innovations.

SanPiN for children with disabilities
The state has also developed and approved sanitary and epidemiological rules and norms (SanPiN 2.4.2.3286-15) for children with disabilities, which are also introduced from September 1 of this year. According to these standards, schools should be provided with special equipment for teaching people with disabilities. Equipment for bathrooms, sinks, porches, entrance doors and entrances to the school, classrooms for children with one or another type of violation is provided. For example, for blind and visually impaired children, desks should be placed closer to the blackboard, and for children with NODA, the distance between desks should be significantly increased. The location of the educational institution is also negotiated in SanPiN, how the territories adjacent to the building, recreation, transitions between buildings, wardrobes, booths for storing clothes should be equipped. Separate chapters prescribe what lighting, water supply, sewerage, as well as daily routine and nutrition should be.
According to the above SanPiN, the maximum occupancy of classes of children with disabilities is determined. The number of such children depends on the type of education and the type of health disorder. So, for example, there should be no more than two deaf children studying according to the 1st option, when a student with disabilities does not lag behind his peers and fully copes with the program, with a total occupancy of 15 people. If the same deaf person is studying according to the second option, when the terms of his education are extended due to poor progress compared to healthy peers, then the class will be filled with 6 deaf children. Studying according to the third option - education does not correlate with the achievements of classmates, there will be 5 deaf children in the class. Option 4 (for children with multiple disabilities), when education does not correlate with the achievements of peers at the end of schooling, assumes that there can be 5 deaf children in a class. Options for all categories of HIA are given in the table.
|
HIA category |
Options for educational programs |
||||
|
1st option |
2nd option |
3rd option |
4th option |
||
|
number of students |
|||||
|
Deaf students |
No more than 2. In total, in a class with 1 deaf student - no more than 20 students, with 2 deaf students - no more than 15 |
||||
|
Hearing-impaired and deaf children |
No more than 2. Total in a class with 1 hard of hearing or late deafness - no more than 25 students, with 2 hard of hearing or late deafness - no more than 20 |
I department: 8 II department: 6 |
Option not available |
||
|
Blind schoolchildren |
No more than 2. In total, in a class with 1 blind - no more than 20 students, with 2 blind - no more than 15 |
||||
|
visually impaired students |
No more than 2. Total in the class with 1 visually impaired - no more than 25 students, with 2 visually impaired - no more than 20 |
Option not available |
|||
|
Children with Severe Speech Impairment (SLD) |
No more than 5. Total in the class - no more than 25 students |
Option not available |
Option not available |
||
|
Schoolchildren with disorders of the musculoskeletal system |
No more than 2. Total in the class with 1 student with NODA - no more than 20 students, with 2 - no more than 15 |
||||
|
Students with mental retardation (MPD) |
No more than 4. Total in the class no more than 25 students |
Option not available |
Option not available |
||
|
Students with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) |
No more than 2. Total in the class with 1 with ASD - no more than 20, with 2 students with ASD - no more than 15 |
No more than 2 in a class of no more than 12 people |
No more than 1 in a class of no more than 9 people |
No more than 1. With a total class size of no more than 5 students and no more than 2 students with ASD in a class with children with mental retardation |
|
|
Children with mental retardation (intellectual disabilities) |
|||||
Working with healthy students
Healthy children are not always ready to understand and accept children who are not like themselves into their team, since their social stereotype of a person is based on personal experience. They do not have sufficient ideas about what could be otherwise, therefore, schools will develop areas of work to overcome stereotypes and change the attitude of healthy children to children of the “disabled” category. For this, mass media materials will be used, which tell about the uniqueness of each person, educational work will be carried out in families, kindergartens and schools. At the lessons in the form of a game, various situations will be simulated that tell about the life of disabled people, video films will be shown, competitions will be held explaining that these children are the same people, but only with disabilities.

Working with parents
GEF for children with disabilities is focused primarily on the family. Teachers and parents act as partners, therefore organizational forms of work with the child's family are planned. For the upbringing of a schoolchild with special educational needs in the family, close people need, first of all, to engage in self-education. Every parent needs to learn to accept their child for who they are and be a bit of an educator. But not all parents want to be involved in the education and development of such a child, so the school staff will have to do a lot of educational work, involving mothers, fathers, grandparents in solving correctional and developmental tasks, implementing individual programs. The teacher, speech therapist and psychologist should provide professional help in matters of education and the choice of a relationship strategy, taking into account the structure of the defect, the age and individual characteristics of the student. And also to carry out preventive work to prevent secondary and tertiary deviations in the development of children with disabilities, the choice of the optimal mode of work and rest in order to avoid overload.
Close cooperation between the parents of a sick child and the school involves conducting surveys of family members, individual and educational consultations for parents, questioning, explaining the stages of AOOP, demonstrating corrective techniques, exercises and tasks, discussing the results of work, joint artistic creativity parents and children: making crafts, participating in exhibitions and theatrical performances. The system of work with parents should become part of the AOOP for a child with disabilities. The results of learning, as well as the degree of motivation of the child for learning activities, will largely depend on the activity of parents.
Julia Savelyeva