The study is necessary to determine the causes of the development of urolithiasis, the choice of tactics for further treatment.
Where can I do a chemical analysis of the stone
 Chemical analysis of kidney stones is done by specialized laboratories.
Chemical analysis of kidney stones is done by specialized laboratories.
Classical medical institutions do not study the composition of kidney stones.
They send the material to specialized laboratories at pathological bureaus or research institutes.
X-ray analysis of a kidney stone can be done not only in the laboratory. Urates and oxalates (calculi based on uric and oxalic acid) are visualized on x-rays. Often they contain calcium ions, which are also visible on the x-ray.
Employees of the X-ray departments do not have knowledge regarding the composition of renal calculi. Chemical analysis is not included in their functional responsibilities.
Determination of the structure is possible when performing survey urography. The procedure is prescribed for urolithiasis to study the structure, contours, shape of the urinary tract.
In Moscow, you can professionally examine the composition of calculi at the Research Institute of Urology. In St. Petersburg, such a service is provided to the population by the Center for Remote Lithotripsy.
Some industrial institutions working with granite, ceramics, crushed stone can analyze kidney stones using the following methods:

- thermogravimetry;
- Spectroscopy;
- Dry and wet chemistry;
- Neutron activation research;
- Chromatography;
- Determination of porosity.
Spectroscopy is a method that is based on the analysis of the degree of absorption of the light spectrum by the sample during the passage of infrared light. The study is rational in case of multistructural formations.
Polarizing microscopy is carried out in the laboratory. The procedure involves studying the reflection of a light beam incident on an object in different planes by a calculus. The polarization of substances of different degrees of density is different, which allows you to determine the structure of the object.

With the help of dry chemistry, mineralization of the stone (ashing) is carried out. Its structure is then examined by dry chemistry. In this case, the sample is crushed and dried on paper. The stone is divided into parts, which allows you to explore the structure of the core, consistency, heterogeneity.
To make thermogravimetry of renal calculi in Moscow offers "Labtest" on Tishinsky Lane. The method is rational to use for industrial purposes. Medical chemical analysis is more convenient and cheaper to carry out by alternative methods.
Thermogravimetry is a method of recording the change in the weight of a sample under the influence of different temperatures.
Determining the porosity of a dried object helps to determine the type of calculus, but does not allow studying the composition of multiple calculi. It is rational to combine the method with chromatography - the division of an object into separate parts, distinguished by their physicochemical properties. By distributing substances between two media (gas-liquid, solid-water), a chemical analysis is carried out.
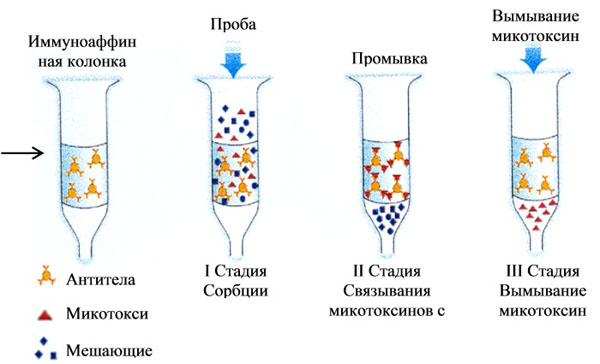
liquid chromatography method
A neutron activation study helps to identify small inclusions in the structure of a sample when a substance is bombarded with neutrons.
The above methods are of historical importance. Medical practice shows that X-ray diffraction analysis and a number of procedures are sufficient to study the structure of the calculus:
- Sediment microscopy (to detect small inclusions);
- Assessment of the acid-base level of urine;
- Bacteriological culture of urine;
- Test for cystine (study of cystine stones).
Urolithiasis is a disease that is characterized by the formation of kidney stones from substances that are part of the urine. When the disease appears, kidney stones are analyzed. What tests for urolithiasis are the diagnostic standard? Find answers to this and other questions below.
Urolithiasis and kidney stones: causes of the disease
Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, in which stones are formed from the composition of the urine, is called urolithiasis. It has many subspecies, differing in the cause of occurrence, nature, size and location of the formation. Analyzes allow you to accurately determine the nature of the stones in order to prescribe effective treatment.
There are many reasons for the development of urolithiasis: these are violations metabolic processes in the body, and anatomical abnormalities of the ureters, and a hereditary factor, and external causes, such as unfavorable environment, water, food. The latter factors affect the composition of urine and its acidity, and are decisive in the composition of the formed stones. In turn, the stones may contain calcium phosphate, calcium oxalate, uric acid, cysteine, magnesium ammonium phosphate.
Urolithiasis and kidney stones: symptoms of the disease
With urolithiasis, stones appear in all parts of the urinary system: in the renal pelvis, ureters, calyces, bladder, and urethra. Stones appear most often in one of the kidneys, but a bilateral process can also occur. There may be one stone in the kidney or urinary tract, but sometimes there are several stones. The size of the stones is very diverse - from small ones about 1 mm to giant ones with a diameter of more than 10 cm. Some stones in patients can exist for a long time without increasing in size, while others can grow to large sizes in 6 months and fill the cups in kidney and entire pelvis. Stones in a third of patients are formed repeatedly, and then the disease becomes recurrent.
Diagnosis of the disease and analysis of kidney stones
Analysis of kidney stones shows that in their structure they are:
Uric acid - consist of yellow-brown uric acid salts, dense, with a rough or smooth surface;
Oxalate - consist of oxalic acid salts of black-brown color, with a rough surface on which there may be spikes, these stones are dense;
Phosphate - soft stones crumble easily, gray-white in color;
Mixed - the inner part of the stones is formed from one type of salt and is called the core, and the shell is from another type of stones;
Cystine are the hardest stones, have a smooth surface.
For kidney stones general analysis urine may show the presence of blood. In addition, it can also detect signs of a urinary tract infection, which in this case is a complication of kidney stones. In the presence of complications, such as the addition of an infection, leukocyturia, an increase in ESR, and a shift in the leukocyte formula can be detected in the blood.
What tests are performed for urolithiasis?
Analyzes for urolithiasis may differ during periods of remission and during renal colic. If remission is characterized by normal tests, then exacerbation is characterized by toxic granularity of neutrophils, shifts in the leukocyte formula and an increase in ESR.
Often in the urine with urolithiasis, an increased content of amino acids, as well as dysuria, is determined. If, in addition to stones, there is an infection in the genitourinary system, then tests are taken for its sensitivity to various antibiotics.
In addition to clinical diagnostics, there are modern express tests to determine urolithiasis. For their implementation, special maps are used that allow you to determine how intense the process of stone formation and their chemical composition. This test allows you to determine not only the presence of stones, but also the predisposition to their appearance, before they form. This is a very important step in the prevention of the disease, since with the help of gentle treatment, the use of herbs, visits to water resorts and special diets, the appearance of kidney stones can be completely prevented.
Since the disease can be asymptomatic for a long time, do not neglect the doctor's recommendation to take a test for the formation of stones. This simple and inexpensive manipulation in the future can save your health and large sums money to restore it.
Urolithiasis of the kidneys (UCD) sometimes asymptomatic, especially in initial stage, although often the presence of stones and sand in the kidneys can be detected using general and daily urinalysis, as well as, clinical and biochemical blood tests and a number of other diagnostic methods.
Each patient with urolithiasis of the kidneys where possible, the chemical composition of the stone should be investigated. In addition, be sure to do a blood test and urine tests. With kidney stone formation, as a rule, salt crystals are present in the urine, which make up kidney stones, this helps to determine chemical composition of kidney stones and prescribe appropriate treatment.
However, to determine the size of the stone in the kidney or ureter and its position, as well as the presence of structural changes caused by the stone, more complex research methods are used.
Methods for diagnosing urolithiasis of the kidneys
The following modern diagnostic methods help to detect kidney stones:
- general and chemical analyzes of urine (control over the level of acidity and excreted salts);
- survey radiography of the kidneys (overview image of the abdominal organs and kidneys);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the kidneys (with regular examination, you can track the dynamics of the growth of kidney stones);
- excretory urography (EU) using a contrast agent (not all stones are visible on x-rays);
- multislice computed tomography (native MSCT without contrast enhancement);
- screening coagulogram (when planning surgery).
To find out exactly what kind of kidney stones you have, you need to contact a urologist or nephrologist who will prescribe a comprehensive examination.
Timely consultations and involvement of an appropriate specialist (endocrinologist, nutritionist, gastroenterologist) in the treatment of KSD are extremely important.
Tests for kidney stones
All patients with suspected nephrolithiasis And urolithiasis appoint general urine analysis to detect inflammatory processes in the kidneys and urinary tract, determine the pH level of urine and other changes, as well as, urine culture for bacteria to detect the presence of a bacterial agent.
Analysis of morning urine with sediment examination
The study is carried out using test strips, determine: urine pH; the number of leukocytes and bacteria; cystine concentration.
Study of daily urine analysis
- calcium;
- oxalates;
- citrate;
- urates (in samples that do not contain an oxidizing agent);
- creatinine;
- volume of urine (diuresis);
- magnesium (additional analysis, necessary to determine the ionic activity in CaOx products);
- phosphates (additional analysis is necessary to determine the ionic activity in CaP products, depends on the patient's dietary preferences);
- urea (additional analysis, depends on the patient's dietary preferences);
- potassium (additional analysis, depends on the patient's dietary preferences);
- chlorides (additional analysis, depends on the patient's dietary preferences);
- sodium (additional analysis, depends on the patient's dietary preferences).
Determining the composition of kidney stones is the first step in treating this disease. Since urolithiasis has different forms of treatment, from medical to surgical, determining the composition becomes an important step in treatment.
To find out what kidney stones are made of, you need to take tests. You should not self-medicate and self-diagnose, as there is a high risk of making a mistake and with certain types of stones this mistake can be fatal.
In my practice, I often encounter situations where the patient prescribes treatment for himself and tries to determine the composition of kidney stones himself, and then you have to deal with complications, and this is at best.
Therefore, if you have symptoms of kidney stones, be sure to contact a specialist and get tested, and then you can choose the treatment, and this article will help you with this.

Kidney calculi may contain organic or mineral substances, or both at the same time. More than 65 different substances have been found, including 25 of them of exogenous origin, i.e. introduced into the human body from the environment.
A comprehensive analysis of the composition of kidney stones has led to the creation of a classification of calculi, according to which they divided into 7 types and 21 subtypes. An interesting fact is that the same chemical component can form a different subtype of stone.
For example, calcium oxalate monohydrate (wevelite) or calcium oxalate dihydrate (wedelite) can be formed from calcium and oxalates. Thus, with proper analysis of the calculus, not only the chemical component that is part of its composition is established, but also the form of its crystallization.
Most of the stones have a mixed composition.
In addition, the core, middle and outer layers are distinguished in the structure of the calculus. The study of the chemical composition of each layer of the calculus can provide very important information about the reasons for its formation.
For example, the core of the stone may be formed by calcium oxalates, and the outer layer may be represented by a struvite component, which may indicate an infection. Quantification of all chemical components that make up the calculus is necessary to provide complete diagnostic information.
You can read more about the chemical composition of stones in the article "".
Determination of the composition of kidney stones

If you think you have a kidney stone. seek help from your doctor or make an appointment with a urologist. They can advise you on how to obtain a calculus for analysis.
As a rule, the doctor advises passing the stream of urine through a mesh filter or a thin cloth when urinating. Sometimes in pharmacies you can find a special strainer for collecting stones.
It is very important to pass the first portion of morning urine through a strainer, because it is not uncommon for a calculus to move into the bladder overnight.
After emptying Bladder check the filter carefully. The stone may be tiny grain of sand or a small piece of gravel. Any calculus you find should be dry, do not leave it in liquid or urine.
Put it in a cup with a lid or a plastic bag. Take it to the doctor's office or laboratory for analysis.
How is the composition of kidney stones determined?
Once the stone is in the laboratory, it is prepared for analysis.
We list only some methods for determining the composition of kidney stones:
- spectroscopy,
- polarizing microscopy
- wet and dry chemical analysis
- x-ray structural analysis
- thermogravimetric analysis
- porosity determination
- chromatography
- neural activation analysis
- nuclear magnetic resonance, etc.
The names sound intimidating and perhaps we shouldn't go into a detailed description of them! However, by this we want to say that thanks to modern equipment and high-tech methods, it is currently possible to determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of any stone, even the smallest one, with high accuracy.
Types of kidney stones
The first thing that a patient with urolithiasis needs to know is what types of kidney stones are, and to determine what type of foreign bodies in his body are. Because the success of treatment depends on their composition. And in order to find out, you need to see a doctor who will prescribe the necessary tests.
Types of kidney stones depending on the chemical composition
The type of kidney stone is determined by its chemical composition. The chemical composition of the calculus can be varied. More than two hundred substances have been identified that have ever been found in stones. However, four types of kidney stones are most common: calcium, urate, struvite, and cystine.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- X-ray methods (survey and contrast radiography);
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- cystoscopy;
- radioisotope nephroscintigraphy.
Ultrasound of the kidneys is used as one of the main methods for diagnosing kidney stones. With this method, it is possible to assess the anatomical changes caused by the presence or advancement of the stone. The disadvantage is the difficulty in detecting stones in the ureters, as they are located deep in the retroperitoneal space.
X-ray examination is the main method for diagnosing kidney stones. If nephrolithiasis is suspected, an overview x-ray is first performed.
When analyzing a plain radiograph, it is possible to determine the presence and number of kidney stones, as well as their size and shape. It should be borne in mind that some types of stones are "invisible", or X-ray negative (urates, cystine stones).
If stones in the kidneys were not detected, but there are clinical symptoms of the disease, then a contrast radiography of the kidneys is performed. The contrast agent is administered intravenously or retrograde through catheters.
Kidney calculi are visible in the form of defects in the filling of the renal pelvis. Contrast radiography of both kidneys and ureters is required in all cases of nephrolithiasis in addition to the plain image.
This method allows you to accurately find out what kidney stones look like, determine their localization, suggest the presence of complications of nephrolithiasis and congenital anomalies of the urinary system, which could contribute to stone formation. In unclear cases, additional sighting pictures of each kidney and ureters are taken.
CT and MRI methods have great importance for the diagnosis of X-ray negative calculi and the differential diagnosis of nephrolithiasis with other diseases. Cystoscopy is not of great value in making a diagnosis, it is mainly used when a stone is suspected in the ureter.
With radioisotope nephroscintigraphy, a radiopharmaceutical is injected intravenously, which is excreted by the kidneys. The kidneys are then scanned and their function is assessed. The study is important for diagnosing complications of nephrolithiasis.
Urate kidney stones
These stones most often occur when there are disorders in the digestive system or with tubular pathologies of the kidneys, when there is an excess of uric acid in the body.
Outwardly, they look like smooth, yellow-orange solid crystals.
Struvites can form only in an alkaline environment affected by infection.
Thus, the main reasons for the formation of struvite stones are:
- alkaline reaction of urine;
- the presence of certain bacteria in the urinary tract.
Struvites are characterized by the ability to rapidly increase in size, filling the entire cavity of the kidney and provoking complications such as sepsis and acute renal failure. It is also worth noting that struvite tends to form in women.
During therapy, it is important that the smallest particles of stones leave the body. Otherwise, the disease will reappear.
cystine stones

A rather rare type of stones, the cause of the formation of which is a genetic pathology - cystinuria.
Children and people at a young age are most susceptible to the appearance of cystine stones.
The cause of stone formation is hereditary cystinuria. which is manifested by a sharply reduced reabsorption of cysteine in the renal tubules. Since this is a hereditary disease, it manifests itself quite early, in young people and even in children.
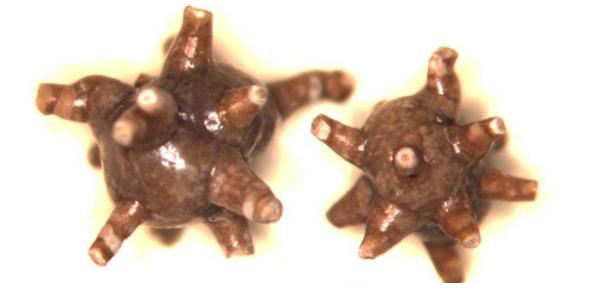
xanthine stones
The cause of the disease is a genetic defect that leads to a deficiency of the enzyme xanthine oxidase, as a result of which xanthine is not converted into uric acid, but is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. It is a poorly soluble substance that tends to crystallize in the urine.
The disease is detected at an early age, the stones are not visible on radiography, but are clearly visible on ultrasound, they are not amenable to conservative treatment.
If medical treatment fails, then the stones are crushed using ultrasound (lithotripsy) into smaller components. When the stone is very large and in acute cases of renal colic, emergency surgery is indispensable, since there is already we are talking about saving the kidney.
To prevent kidney stones from being recurrent, the patient's task is to stop and prevent stone formation. For the sake of health, it is worth completely changing your lifestyle and radically reviewing your diet.
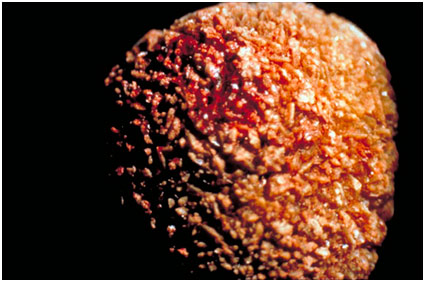
oxalate stones
are stones formed from calcium salts of oxalic acid. They are much more common than all other species.
Oxalate stones are black-gray in color, very often with thorns, like hedgehogs (see photo of an oxalate stone), which injure the urinary tract mucosa, which leads to urine staining red.
Based on the fact that oxalate stones are stones derived from oxalic acid, we conclude that they will most often form with its increased intake into the body.
The most dangerous foods for people who have oxalate stones, it is their excessive consumption that increases the chance of the formation of this type of kidney stones: various sweets, chocolate, muffins, cocoa, beets, lettuce, sorrel, spinach, parsley and others.
Oxalates are of a very hard consistency, their dissolution with medicines and with the help of traditional medicine is not possible. Such stones are either crushed using contact or remote lithotripsy, or operated on.
If the kidney stone is up to 6 mm in size, it has every chance to go out on its own. Oxalate kidney stones are clearly visible on x-rays (in the form of a white shadow), because excretory urography in this case is very informative.
Phosphate stones

Phosphate kidney stones are also formed from calcium salts, but phosphoric acid, unlike oxalates. The color of the stones is light gray or white.
Their surface is smooth, and the sizes and shapes are very diverse. Phosphate kidney stones are quite soft, very easily crushed by ultrasound, and can dissolve if the pH of the urine increases.
This type of kidney stones is formed when the urine is alkaline (Ph above 6), which often happens with chronic inflammatory diseases kidneys, bladder, metabolic disorders. Phosphate kidney stones grow very quickly, in some people they come out in dozens per month, and new ones form again.
Indirectly, it can be judged that a person has a kind of phosphate kidney stones - if the urine has acquired a white cloudy color, white flakes often fall out in such urine.
The treatment of phosphate stones comes down, first of all, to the prevention of inflammation of the kidneys and bladder, as well as to the acidification of urine. If you acidify urine (bring its Ph to a level below 6), unfavorable conditions will be created for the formation of phosphate stones.
The diet for phosphate kidney stones should include: lard, meat (especially fatty varieties), fish, sunflower oil, flour products, sour juices (lingonberry, cranberry). From drinks, it is necessary to brew the root of grapes, rosehips, barberries, consume at least 2-2.5 liters of liquid per day.
Carbonate kidney stones

This is a type of kidney stones that are formed from calcium salts of carbonic acid. Carbonate stones have a white color, smooth surface, various shapes, and are quite soft. This type kidney stones are quite rare, so I will not describe them in detail.
Mineralogical classification of kidney stones
The mineralogical classification of stones is currently accepted all over the world. The main types of kidney stones:
- Inorganic calcium compounds - the most common 80%, phosphates, oxalates;
- Uric acid stones - urates 15% and the older the patient, the more common these stones are;
- Less common are protein stones - xanthine, cystine, indicating a violation in the patient's body of the exchange of the corresponding amino acids;
- Magnesium-containing stones are combined with the appearance in the urine of an infection;
In 50% of cases, stones mixed in composition are formed. Kidney stones can be either single or multiple. The size of the stones is the most diverse, starting from a mass of 0.1 grams and up to 2.5 kilograms or even more, and ranging in size from 0.1 millimeters to 10-15 centimeters.
Best Diet for Oxalate Kidney Stones

Cauliflower and white cabbage, lingonberries, carrots, apricots, eggplants (in moderation), bananas, pears, grapes, pumpkins, cucumbers, prunes, cherries, barberries, soaked herring, coriander greens, potatoes (only boiled), cucumbers, peeled, turnips, apples, apricots, watermelons, melons, peaches, quinces, dogwood and other berries and fruits, birch sap, mountain ash, prunes, dried apricots, pears, squash and eggplant caviar.
Wheat bread made from flour of the 2nd grade, gray, rye, vegetable oil, walnut, hazelnut, pine nut.
Dairy products should be consumed only in the morning! Sour-milk drinks, kefir, sour cream in small quantities, cottage cheese (up to 400 grams per day), fresh curdled milk, butter and Provence oil no more than 60 gr. in a day.
1 egg per day, vegetable soups without adding peas, beans, mushrooms, lentils, beans, sorrel, spinach, parsley and without frying and sautéing flour and vegetables ( the best option- diet cabbage soup from fresh cabbage), fruit soups.
Weak tea, coffee (preferably a surrogate) with milk (no more than 50 grams per day). Meat, poultry and fish of low-fat varieties in boiled, fried and baked form (boil first) - eat 150-200 gr. in a day.
For those who are prone to urolithiasis, urologists advise eating fewer foods containing animal proteins. Dairy, diet types of boiled sausages, unsalted fat in small quantities.
Dishes from pasta and cereals. Add pasta only to soups in small quantities. A lot of vegetables, fruits and berries, except for the above, in raw, boiled, baked form, except for sour varieties (cranberries, antonov apples, gooseberries, red currants).
Non-spicy tomato paste, sweet tomatoes, non-sour sauerkraut, no more than 30 gr. on the day of sugar, kissels, compotes, white sauces that do not contain vinegar. Salt no more than 2 gr. per day.
Diet from Malysheva with kidney stones
Different types of cereals - oatmeal, buckwheat, millet, pearl barley, as well as soups from them. Periodically - potato-cabbage diet. Slightly alkaline mineral waters (2 courses per year).
Pears, apples, quince, infusions of pear tree leaves and peel, as well as grapes significantly contribute to the removal of oxalic acid, and potato dishes alkalize urine, bind calcium and promote its excretion from the body through the intestines.
Cucumber juice is the best and most effective remedy for oxalic acid nephrolithiasis. The body with oxalates must be provided with vitamins A, B2, D and phytin. Such vitamins contain raspberries, carrots, sea buckthorn, apples, black currants. We need to increase our consumption of these products.
Diet - food at least 5 times a day, do not eat cold dishes, increase the volume of liquid to 2 - 2.5 - 3 liters. per day, preferably in the form of juices from fruits and vegetables.
Not allowed for kidney stones
Products containing oxalic acid: chocolate, vinegar, fatty meats, wine berries, sweets, jam, cookies, dough products - rich and puff, ice cream, mustard, tomatoes. These are products containing oxalates in large quantities, which in no case should be eaten.
Meat, fish, poultry and mushroom broths and sauces, gelatin, jelly, jellies, tongue, liver, brains, kidneys and all other animal entrails, canned food and sauces - meat and fish, caviar, sausages (especially liver), pastes, smoked meats, salted fish, fried foods, spicy foods and seasonings, salty cheeses, very sour foods and foods, lamb, beef, cooking fats (limit pork fat).
From vegetables and herbs, you can not eat mushrooms, peas, beans, peanuts and other legumes, fried potatoes, spinach, sorrel, lettuce, parsley, beets, asparagus, rhubarb, Brussels sprouts and red cabbage, broccoli, figs, radish, celery, lentils, horseradish , nettle, bell pepper and pepper in the form of seasoning, leek.
From berries and fruits, exclude all those that contain a significant amount of vitamin C - red currants, plums, all citrus fruits, gooseberries, strawberries, blueberries, cranberries, dried grapes (raisins), radishes, Antonov apples.
From drinks exclude strong tea, cocoa, bread kvass, chicory, tomato juice.
Information about the types of kidney stones from the medical guide
The definition of urinary stones is carried out according to the following scheme:
I. According to the experimental value of the density determined in vivo by the method of spiral X-ray computed tomography (H value), the possibility of the formation of a single-phase urinary stone is first estimated according to the values of H found by us for individual components (Table 1), and then two-phase.
The latter is verified by our experimental and calculated data (Table 2). Thus, at this stage, either the composition of a single-phase urinary stone is determined, or the composition of urinary stones is assessed in the case of a two-phase mixture and the most probable compositions are distinguished.
II. According to the experimental value of the density determined in vivo by the method of helical X-ray computed tomography (H value), the value of ρ, g/cm3, is calculated by formula (1), which is the X-ray density.
Based on the value of ρ, using the known values of ρi for the individual components of urinary stones, the composition of the two-phase mixture is estimated using the additivity formula ρ=x1ρ(1)+(1-x1)ρ(2) (2).
III. The analysis of the obtained compositions of urinary stones is carried out using biochemical data (urinalysis) and fluoroscopy, which is included in the mandatory examination of patients. Based on the results obtained, the only variant of the composition of the urinary stone is determined.
Method for determining the chemical composition
Knowing the composition of the urinary stone allows the administration of specific drugs that aim to modify the physical properties (eg, decrease in size, hardness, increase in porosity) of the urinary stone, thus optimizing lithotripsy regimens and reducing the risk of kidney injury.
IV. After surgery or lithotripsy, the isolated urinary stone is examined by in vitro radiography to determine and confirm the true composition of the urinary stone. Based on the composition of the urinary stone, treatment is prescribed to prevent possible relapses.
The developed method for determining the composition of non-disintegrated urinary stones (in vivo), i.e. urinary stones in the patient's body, based on the obtained dependence p(±0.07)=1.539+0.000485 N (where N in relative units is the density determined by the method of spiral X-ray computed tomography, ρ in g/cm3, calculated X-ray density) was confirmed during the examination and treatment of more than 100 patients of the Urological Clinic of the Moscow Academy. I.M. Sechenov.
I. Only on the basis of the values of H determined by us (Table 1), several assumptions can be made:
1. Only newberite can be included in the composition of urinary stones. does not form single-phase urinary stones, but is only part of multi-phase stones.
On the other hand, the presence of only Newberite in the composition of the urinary stone contradicts the results of the clinical examination of the patient: urine pH = 6.0 (for Newberite, urinary pH > 7.0) and a clear image of the urinary stone was obtained on x-rays (for Newberite, blurred images are obtained with fluoroscopy) (see Fig. Table 1).
Treatment of urolithiasis is not an easy task. In order to prescribe the correct therapy, it is necessary to analyze the deposits in the kidneys in order to establish their qualitative composition.
Where can I do a chemical analysis of the stone
In order to determine the properties and characteristics of a kidney stone, it is necessary to conduct a chemical analysis in a laboratory specially equipped for this. Ordinary state honey. institutions do not carry out such research. All samples are sent by them to special laboratories operating at pathoanatomical bureaus or research institutes.
Unfortunately, there are not many institutions capable of performing such an analysis, because the study requires special expensive equipment and special training of personnel.
Some types of deposits (urates and oxalates) can be seen on x-rays. These formations may contain calcium ions, which is also visually seen on the radiograph. Such a study is carried out in a regular state clinic.
Employees of X-ray rooms do not have knowledge about chem. composition of kidney stones. This is not part of their responsibilities.
You can conduct a professional study of kidney formations at the Research Institute of Urology in Moscow or at the Center for Remote Lithotripsy in St. Petersburg.
Preparation for chem. analysis
Performing such a study does not require any special preparation. To carry it out, you only need a sample of a kidney stone. To obtain it, you simply need to collect urine after renal colic, upon completion of the procedure for crushing stones in the renal pelvis, or after removing a stone from the kidneys by surgery.
- When urinating, a portion of urine is passed through a filter (it is easy to buy at a pharmacy) or through a thin, clean cloth.
- Upon completion of the procedure, the filter (fabric) must be carefully examined. A kidney stone can be a tiny, barely noticeable grain of sand.
- The resulting material should be put in a jar with a lid. It is important to remember that the sample must be dry.
- It remains to hand over the contents of the container to the laboratory or to the attending doctor.
How the study is done
After a kidney stone enters the laboratory, a chemo is performed. study in one of the following ways:
- Spectroscopy is a method based on the analysis of the degree of absorption of the light spectrum during the passage of infrared light. This method is best suited for the study of multistructural formations.
- Polarizing microscopy is a procedure carried out exclusively within the walls of the laboratory. It is based on the study of data obtained when a calculus reflects a light beam incident on an object in different planes. It will be possible to establish the structure of the stone due to differences in the polarization of substances of different degrees of density.

- Dry chemical analysis involves the procedure of mineralization of the provided material. You should start by grinding and drying the calculus on paper. Moreover, its division into parts makes it possible to study the structure of the nucleus, consistency, and heterogeneity.
- X-ray diffraction analysis
- Neuronal activation data make it possible to establish the presence of the smallest inclusions in the structure of a kidney stone during the bombardment of deposits by neurons.
- Determining the porosity of a dried stone makes it possible to identify its type, but at the same time excludes the possibility of studying the composition of multiple formations. The best option is the compatibility of this method with chromatography.
- Chromatography is the separation of a kidney stone into separate parts that differ in physical and chemical properties.
- Thermogravimetric analysis is based on observations of the change in the weight of a sample when exposed to different temperatures.
According to medical observations, to examine the structure of the deposit it is enough to carry out X-ray diffraction analysis and some other procedures described below.
Determining the composition of stones indirectly
Since it is not always possible to obtain stones for analysis, there are simple diagnostic methods that help to establish a chemical with a high degree of probability. composition of stones in an indirect way. Similar methods include:
- X-ray description of education. If the stone is clearly visible in the picture, then it is most likely calcium. Cystine and struvite stones are characterized by poor contrast. And urate and xanthine formations are generally not visible on the radiograph.
- Microscopic analysis of urine sediment to determine the presence of microliths (small crystals that are the basis for the growth of stones).
- Chem. study of urine acidity. In an acidic environment, mainly urate stones appear.
- Bacteriological examination of urine. The presence of bacteria is an undeniable risk factor for the formation of proteinaceous and mixed deposits.
- Samples for cystine make it possible to judge the presence of cystine stones.

Survey results
Based on the results of the examination, a conclusion is given as to what chemical composition the calculus from the kidney has.
There are several types of kidney deposits:
- Calcium or oxalate. This type of stones is the most common (about 80%). The name speaks for itself. These formations are based on calcium salts.
- Struvite stones, composed of ammonium phosphate, the incidence is about 15%.
- Urate stones are formed by salts of uric acid (5–10%).
- Cystine stones are rare - 1-2%.
- Protein, mixed - about 1% occurrence.
Having carried out chem. analysis of a calculus from the kidney, the attending doctor will be able to draw appropriate conclusions regarding the cause of the formation of deposits, outline further examination and make the right decision regarding treatment. In addition, carrying out chem. analysis of deposits, makes it possible to choose the most effective preventive measures in the issue of the formation of kidney stones.