Inflammatory diseases in women are accompanied by symptoms, which can be used to suggest the presence of a specific disease and prescribe an adequate diagnostic examination, and subsequently treatment. An increase in temperature often accompanies inflammation in the female genital area, being an important signal. And this signal must be responded to in a timely manner.
What does an increase in temperature in gynecology indicate?
An increase in temperature along with other symptoms (pathological discharge from the genital tract and lower back, sexual dysfunction, etc.) is often a sign of an inflammatory disease. Most often, such a symptom manifests itself in the acute form of the disease, but a slight increase in temperature is also possible in subacute and chronic forms. Sometimes inflammation is not accompanied by an increase in body temperature, which in some cases makes it difficult to make a diagnosis.
There are many reasons for the development of inflammation - from non-compliance with the hygiene of the genital organs to the usual decrease in a woman's immunity.
Inflammation can develop both in the lower genital organs and in the pelvic organs. Let us consider in more detail what inflammatory diseases can affect female organs.
An increase in temperature with inflammation of the lower genital organs
There are a number of inflammatory diseases, sometimes accompanied by a slight increase in temperature (37.2 - 37.5ºС), more pronounced (from 37.6ºС) or without this symptom at all.
- Candidiasis, which is an inflammation of the vagina caused by fungi of the genus Candida. characteristic feature, which makes it possible to assume a disease - curdled discharge from the genital tract with a sour smell. Diagnosis using a smear study clearly determines the pathogen, and the antibiogram - its sensitivity to different groups of antibiotics.
- - also inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, however, developing due to a different kind of microorganisms (staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, etc.). At the same time, an examination by a gynecologist and sexual intercourse can cause extremely unpleasant sensations.
- - inflammation of the external genitalia and vagina develops. The disease can be both infectious and non-infectious in nature (allergy to latex, lubricants, mechanical and chemical damage).
- Cervicitis - this disease is in question when inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal of the cervix develops. It often accompanies other diseases of the internal genital organs, vagina or cervix.
- Urethritis - inflammation of different parts of the urethra develops.
- - inflammation of the glands of the vestibule of the vagina is detected.
What diseases of the pelvic organs are accompanied by fever
The most common are inflammatory diseases internal genital organs of a woman, which in frequent cases cause an increase in temperature:
- Salpingoophoritis - an inflammatory process affecting the uterine appendages (ovaries, tubes);
- - inflammation in the uterine mucosa;
- Pelvioperitonitis - inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum develops. It can occur due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms from the fallopian tubes or due to the rupture of purulent formations.
Just like other symptoms, fever is a frequent, but optional companion of inflammation of the female organs. Therefore, the presence of other signs of possible disorders, even without temperature, should be the reason for contacting a gynecologist.
There are many different types of colds. Among the people there is also a cold of the genital organs. What disease is hidden behind this designation in fact?
Symptoms of the development of a cold of the genital organs in women
Illness is never on time. In addition, it is very unpleasant to lie in bed with cold symptoms - cough, runny nose and high fever. But strangely enough, it is not the disease itself that is dangerous, but the consequences and complications of a cold. One of the varieties of the disease, or rather its consequence of excessive hypothermia, is inflammation of the female genital organs.
There is literally no such disease as the common cold. Because neither the kidneys, nor the ovaries, nor the appendages can catch a cold. Here we are talking about the inflammatory process, which can be triggered by an infection or hypothermia respiratory tract. Inflammation can be both acute and chronic.
Colds in women have pain symptoms:
- in the sacrum
- in the lower abdomen, which are aggravated by physical exertion.
- Sometimes this pain radiates to the hips.
- Also during this disease, body temperature may rise.
- There can be many unpleasant consequences if treatment is not started on time.
The disease, like any other inflammatory process, can develop rapidly and end very badly. Therefore, it is very important to detect it at the earliest stages and treat it completely.
The cause of the disease is always an infection that occurs as a result of non-compliance with the rules of hygiene of sexual life and personal hygiene. A female cold can be provoked by an infection brought into the ovaries from the fallopian tube, intestines or peritoneum. Douching with cold water, a common cold or hypothermia can trigger an infection. If the treatment of acute inflammation is not started in time, a cold of the genital organs can turn into a chronic form.
Symptoms of a female cold with endometritis
Endometritis (colds of the lining of the uterus). In acute inflammation of the uterine mucosa, there is a high temperature, pain in the lower abdomen, often radiating to the hips and sacrum. This type of female cold begins with the release of whites, at the first stage they are normal, white in color, and then they begin to take on a yellowish-dirty appearance and have a characteristic, unpleasant odor. In the future, these secretions turn into purulent and fetid.
In the chronic form of a cold of the genital organs, women have a menstrual disorder. The main cause of this type of female cold can often be gonorrhea or some kind of infection brought by non-sterile instruments, as well as hypothermia of the lower abdomen or a consequence of an abortion.
Signs of a cold of the genital organs with oophoritis
A female cold of this type is usually expressed in a violation of the function of these organs. Microbes of infection in the ovaries can be brought from neighboring organs, as well as through the lymphatic and blood vessels. Colds of the ovaries in women constantly occur simultaneously with inflammation of the fallopian tubes adjacent to them. Often, acute inflammation subsequently flows into chronic illness. Inflammation may be favored by non-compliance with the generally accepted rules of hygiene of sexual life and personal hygiene.
In the acute stage of a cold with oophoritis, the pain is quite pronounced, especially in the lower abdomen. Quite often, the pain takes on a cramping character. In the chronic stage of this type of disease, patients are disturbed by dull pains that intensify during menstruation along with an increase in body temperature and physical stress. Typically, pain symptoms appear in the hips and sacrum. If the necessary measures are not taken, then irregular and painful menstruation will certainly begin, and sometimes an abscess forms in the ovaries, which can reach a significant size.
How to treat a female cold at home?
A mandatory measure is the delivery of tests and contacting a specialist. After determining the infection that caused the disease, you will be prescribed the appropriate treatment. Alternative treatment of this disease is possible and very effective.
Potassium iodide and mud baths will help with the chronic form of the genital cold. Also useful in the treatment of genital colds are hot douches.
Cleansing the stomach, in which castor oil should not be used, because it can increase pain and cause bloating. After cleansing, put an ice pack on your stomach and stay in bed, especially if you have a fever.
Lubrication of the abdomen with Ichthyol ointment or Ichthyol.
Complete cessation of sexual activity until cessation pain.
During treatment, pumpkin juice, pumpkin dishes should be included in the diet, and a decoction of the “hair” of corn cobs also helps.
The most important thing is to notice the disease on initial stage. For the treatment of a cold of the genital organs in women, peace is needed, as well as an immediate appeal to a specialist doctor. In order to relieve pain, it is necessary to eat asparagus as much as possible, which in turn is useful for any diseases of the uterus. It is also possible in folk treatment douche the vagina with a solution of tannin.
Causes of colds of the genital organs in women
Every woman in her childhood has heard truthful “calls” more than once not to sit on cold surfaces, for example, on window sills, in winter on benches or on a concrete floor. After all, in this way you can get serious hypothermia and, as a result, flu, acute respiratory infections, cystitis, inflammation of the ovaries, appendages, Bladder and other colds.
As a rule, the ovaries take part in the inflammatory process simultaneously with the tubes and other related internal organs. The common cold is usually expressed in violation of the function of these organs. The microbes of this infection in the ovaries can be brought from neighboring organs, as well as through the lymphatic and blood vessels. A cold of the ovaries constantly proceeds simultaneously with inflammation of the fallopian tubes adjacent to them. Often, acute inflammation subsequently flows into a chronic disease. Inflammation may be favored by non-compliance with the generally accepted rules of hygiene of sexual life and personal hygiene.
Acute inflammation of the ovaries can also be caused by cooling the legs during menstruation, a cold, douching with cool or cold water after sex. In the acute stage of a cold in women, the pain is quite pronounced, especially at the bottom.
The main factors of a cold of the genitals in women
The causes of the disease are mainly various microorganisms and bacteria. For example, such as E. coli, staphylococci, gonococci, streptococci, tubercle bacillus and various fungi.
They penetrate the inside of the genital organs, both due to poor hygiene, and due to domestic moments or the illness of a sexual partner.
One of the main causes of the disease is a violation of their integrity. This can occur from strong friction of uncomfortable or tight clothing, when foreign objects are in the vagina for a long time, due to bathing in reservoirs with infectious microorganisms, or due to violation of the rules of antiseptics and disinfection during surgical intervention.
Inflammation of the genital organs is observed mainly in women of childbearing age and women with an active sex life.
- Benign tumors of the female genital organs
- Cervical and uterine cancer
- Signs of ovarian cancer
- Cancer of the vagina and labia
Oncology of the female genital organs can be divided into two groups: benign and malignant. When studying the signs of oncology in a female way, it must be borne in mind that this concept includes not only cancer, but also other neoplasms that are unable to spread throughout the body and form new tumors, however, also requiring timely diagnosis and treatment.
Benign tumors of the female genital organs
The tumor, which has a benign nature, slowly grows in breadth and does not have the ability to metastasize, that is, spread to other organs. Nevertheless, such neoplasms are also considered oncological and require treatment, in the absence of which complications are possible. Gynecology distinguishes the following types of benign neoplasms:
- myoma;
- fibromyoma;
- fibroma;
- ovarian cysts.
- polyps of the body and cervix.
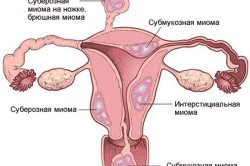
Myoma is a tumor of the muscular membrane of the uterus (myometrium). The reason for the appearance of fibroids is a hormonal imbalance, leading to an increase in estrogen levels, pathologically rapid growth of uterine tissues and the formation of nodes and seals.
You can recognize a tumor of the myometrium by signs: heavy bleeding during menstruation, pain in the lower abdomen. In the absence of treatment and the appearance of complications, patients may experience severe pain in the uterus, suffer from chills or fever.
Fibroma is formed from smooth muscle and connective tissue in the external or internal genital organs, most often in the uterus. Fibromyoma occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance and can reach very large sizes. As the tumor grows, unpleasant symptoms begin to appear: sensations of pressure in the pelvic area, an increase in the amount of menstrual flow.
Fibroma is formed inside the cervix or walls of the uterus from fibrous connective tissue. Sometimes a fibroma appears on the labia, ovaries, or in the vagina. Signs of benign oncology in a feminine way in this case are pain in the pelvic area, difficulty in the processes of urination and defecation.
An ovarian cystoma is a cavity in glandular tissue, often formed from an existing cyst. Oncological studies of cystoma have shown that it is quite dangerous, because it can develop into a cancerous tumor. The first signs of ovarian cystoma: bloating, menstrual irregularities, discomfort. In some cases, spasms and jerking pain are observed, sexual intercourse becomes painful.
Polyps are soft benign neoplasms of red-pink color, located on the mucous membrane in clusters. Polyps on the cervix can be seen with a speculum or recognized by touch. With polyps, there may be an increase in discharge during menstruation, the appearance of bleeding after sexual intercourse.
Back to index
Cervical and uterine cancer
Among the oncological diseases of the female genital organs, the most common is.
Among the main causes of cancer in women are: viral diseases, promiscuous sex life or its early onset, cervical injury, smoking. Often the cause is herpes and papillomavirus, so women of any age are recommended to be tested regularly to rule out the presence of these viruses. There are several stages of cervical cancer:
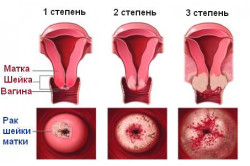
With cervical cancer of the second and third stages, patients often complain of spotting between periods, the appearance of blood in the urine, pain in the legs and back. The first stages of the development of the disease can be asymptomatic, diagnosis is possible only with a gynecological examination.
Cancer of the body of the uterus is characterized by diffuse lesions of the endometrium or a separate polyposis overgrowth. Growing into the uterine tissue, the tumor can spread to the abdominal cavity and appendages. With cancer of the body of the uterus, patients can observe purulent-bloody discharge from the vagina, which has an unpleasant odor. During menopause, bleeding may be a sign of the disease.
Back to index
Signs of ovarian cancer
The second most commonly diagnosed cancer in gynecology after cervical cancer is. The risk group includes older women, especially those who have not given birth. As statistics show, mothers with many children suffer from this disease at times less often. In some cases, the appearance of malignant neoplasms on the ovaries may be due to a genetic predisposition.
Signs of advanced ovarian cancer: bloating, nausea and vomiting, constipation. The appearance of unpleasant symptoms is due to the fact that the tumor disrupts the intestines and causes the accumulation of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites). In the early stages, it may be asymptomatic.



